Parts
Bicycle Gears Explained – Guide to Shifting
In the world of cycling, having the right set of gears is paramount to your riding experience. Whether you’re a seasoned cyclist or just getting started, understanding the various types of bicycle gears is essential. In this comprehensive guide, HookBike’s will take a deep dive into the world of bicycle gears, explaining the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of each type. By the end of this article, you’ll have the knowledge to choose the perfect gear system for your cycling needs.
The Basics of Bicycle Gears
Bicycle gears are an essential part of modern bicycles, allowing riders to adjust their pedaling effort to various terrains and riding conditions. Gears are used to make pedaling easier when going uphill, harder when going downhill, and to maintain a comfortable cadence (pedal speed) on flat terrain. Here are the basics of bicycle gears:
Gear Ratios
Gears are expressed as ratios. For example, a gear ratio of 2:1 means that for every two rotations of the pedals, the rear wheel (and the bike) rotates once. Lower gear ratios (e.g., 1:1) make it easier to pedal, while higher gear ratios (e.g., 2:1) make pedaling harder.
Components
Bicycle gears consist of several key components:
- Chainrings: These are the front gears attached to the pedal crank. They come in various sizes and are responsible for the initial gear selection.
- Cassette or Freewheel: The rear gears are mounted on a cassette or freewheel, which attaches to the rear wheel hub. These gears provide further gear options.
- Derailleurs: The front and rear derailleurs are devices that move the chain between different chainrings and gears to change the gear ratio. Derailleurs are controlled by shifters.
- Shifters: Shifters are levers or buttons on the handlebars that allow the rider to change gears. The right shifter typically controls the rear derailleur (cassette/freewheel), while the left shifter controls the front derailleur (chainrings).
Front and Rear Derailleur
The front derailleur moves the chain between the different chainrings, allowing you to change the front gear. The rear derailleur moves the chain between the different gears on the cassette or freewheel. These components are responsible for precise gear changes.
Chain Movement
When you shift gears, the chain moves from one chainring or gear to another. To prevent the chain from coming off the gears, derailleurs guide it smoothly and securely.
Cadence
Cadence refers to the speed at which you pedal. The ideal cadence depends on your riding conditions and goals. A lower gear (easier pedaling) allows for a higher cadence, while a higher gear (harder pedaling) results in a lower cadence.
See more: Which gear to use when going uphill bicycle?
Cross-Chaining
Avoid extreme chain angles, known as cross-chaining, which can cause wear and damage to the chain and gears. Typically, you should avoid the largest chainring with the largest rear gear, as well as the smallest chainring with the smallest rear gear.
Understanding how to use bicycle gears effectively is crucial for improving your riding experience and overall performance. Practice shifting gears and pay attention to your cadence and the terrain to make the most of your bike’s gear system.

Types of Bicycle Gears
Bicycle gears come in several different types, each with its own advantages and applications. The choice of gear type depends on the type of bike you have and your intended riding style. Here are some of the common types of bicycle gears:
Single-Speed
Fixed-Gear (Fixie): A single-speed bike with a fixed rear wheel, meaning you can’t coast. You must pedal continuously. These bikes are often favored by track and urban riders.
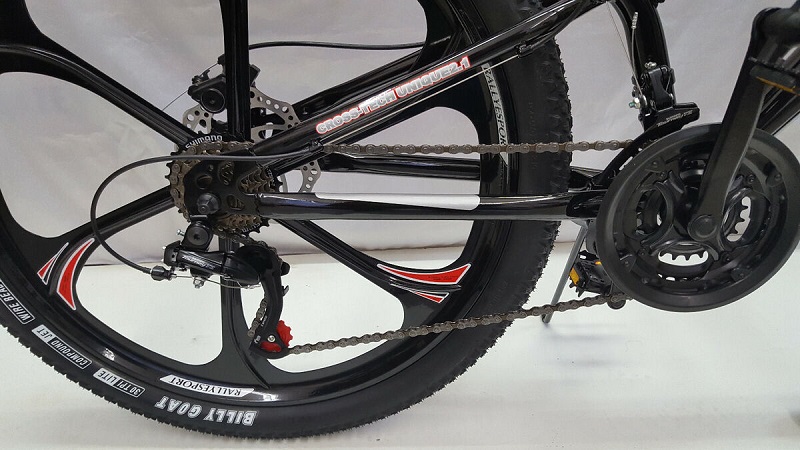

Internal Gear Hub
Bicycles with internal gear hubs have all the gears contained within the rear hub. These gears are enclosed and require less maintenance than external derailleurs.
Common brands for internal gear hubs include Shimano Nexus and Rohloff. They are often found on commuter and city bikes.
Derailleur Gears
- 1x (One-By): A single chainring in the front and multiple gears in the rear. Common on mountain bikes and some gravel and cyclocross bikes.
- 2x (Two-By): Two chainrings in the front with multiple gears in the rear. This setup is commonly found on road bikes, but it’s also used on many other types of bikes.
- 3x (Three-By): Three chainrings in the front and multiple gears in the rear. This setup offers a wide range of gears and is often found on touring and hybrid bikes.
Electronic Gears
Some high-end bikes use electronic shifting systems, such as Shimano Di2 or SRAM eTap. These systems use electronic signals to shift gears, providing precise and reliable shifting.
Belt Drive
Instead of a traditional chain, some bikes use a belt drive system. Belt drives are low-maintenance and don’t require lubrication. They are often found on commuter and urban bikes.
Hub Gears
These are similar to internal gear hubs but may have more gears and are typically found on city and utility bikes. Some hub gears are continuously variable, allowing you to choose any gear ratio within their range.
Mountain Bike Groupsets
There are specialized groupsets designed for mountain biking, with features like wide gear ranges, improved durability, and clutch mechanisms to prevent chain slippage.
Road Bike Groupsets
Road bike groupsets are designed for speed and efficiency, with lightweight components and gearing optimized for pavement riding.
Gravel/Cyclocross Groupsets
These groupsets are designed for mixed-terrain riding, with features that allow for a wider range of gears and the ability to handle rough roads and trails.
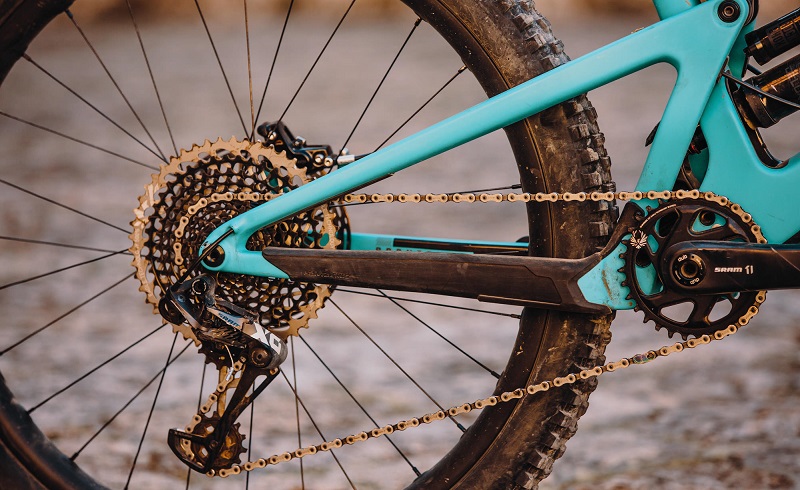

Touring Groupsets
Groupsets for touring bikes typically include a wide range of gears and sturdy components for long-distance and loaded touring.
Hybrid Bike Groupsets
Hybrid bike groupsets are versatile and suitable for a variety of riding conditions, including commuting and recreational riding.
Fat Bike Groupsets
Designed for fat-tire bikes, these groupsets provide gearing that can handle the challenges of snow, sand, and other loose terrain.
The choice of bicycle gear type should align with your riding style, terrain, and preferences. Different types of bikes will come equipped with specific gear systems that suit their intended use, and you can also upgrade or modify your bike’s gears to better match your needs.
Choosing the Right Bicycle Gears
Choosing the right bicycle gears is important to ensure that your bike suits your riding style, terrain, and fitness level. Gears allow you to pedal comfortably and efficiently in various conditions. Here are some steps to help you choose the right bicycle gears:
Identify Your Riding Style
Determine how you plan to use your bicycle. Are you mainly commuting on flat roads, riding on hilly terrain, or exploring trails? Your riding style will greatly influence the type of gears you need.
Understand Gear Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of gears available (e.g., single-speed, internal hub, derailleur, etc.), as each has its advantages and limitations.
See more: Do you shift gears while pedaling?

Analyze the Terrain
Consider the typical terrain you’ll be riding on. If you’ll be tackling steep hills, you’ll need lower gears to make climbing easier. For flat roads, you can opt for a simpler gear setup.
Determine Your Fitness Level
Your fitness level will affect your ability to pedal in higher or lower gears. If you’re a beginner or have lower fitness, you may prefer a wider range of gears to accommodate various intensities.
Choose the Number of Gears
Depending on your needs, select the number of gears that suits you. For example, if you’re riding in a flat urban environment, a single-speed or 3-speed internal hub might suffice. If you want versatility for various terrains, consider a multi-speed derailleur system.
Consider Gear Ratios
Pay attention to the gear ratios offered by the gear system. A wide range of ratios allows for easier climbing and faster riding on flats. Calculate or ask about specific gear ratios to ensure they match your needs.
Test Ride Bikes
If you’re buying a new bike, test ride different models with various gear setups. This will help you get a feel for how the gears operate and whether they suit your riding style.
Consult a Bike Shop Expert
Visit a local bike shop and consult with experts. They can provide recommendations based on your needs and can help you choose the right gear system for your bike or assist with any upgrades.
Understand the Shifting System
Get familiar with how the gear shifting system works on the bike. Learn how to shift gears smoothly to avoid any issues while riding.

Think About Maintenance
Consider the maintenance requirements of the gear system. Derailleur systems, for example, may require more maintenance than internal hub gears. Choose a system that aligns with your willingness to maintain your bike.
Upgrade if Needed
If you already own a bike and find that the current gear setup doesn’t suit your needs, consider upgrading the gear components. Consult with a bike mechanic or shop for guidance on compatible upgrades.
Budget Considerations
Keep in mind that more complex gear systems and higher-quality components may come at a higher cost. Determine your budget and look for a balance between price and quality.
Choosing the right bicycle gears is a personalized process, and it’s essential to consider your unique riding circumstances and preferences. By following these steps and seeking advice when necessary, you can select the right gear setup to optimize your cycling experience.
Conclusion
In the world of cycling, the right choice of bicycle gears can significantly impact your overall riding experience. Whether you’re looking for simplicity, precision, or versatility, there’s a gear system that suits your needs. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with the knowledge to make an informed decision and enhance your cycling adventures. Remember, the best gear system is the one that helps you enjoy your time on the road or trail to the fullest.