Parts
Bike Gear Shifter Types: Explained For Beginners
Bicycles have evolved over the years and so have their components. One of the key elements that determine the efficiency and experience of cycling is the gear shifting system. For beginners, understanding the different types of bike gear shifters is crucial in ensuring optimal performance and safety. In this article, HookBike’s will delve deep into the various Types of bicycle shifters systems, providing a comprehensive guide to help newcomers make informed decisions.
A Brief Overview of Bike Gears
Gearing systems are essential for bicycles, especially when it comes to negotiating a variety of terrains and riding conditions. Here’s a brief overview of bike gears:
Why Gears Matter
- Adaptability: Gears allow riders to maintain a comfortable and efficient pedaling speed (cadence) across a range of terrains—from flat roads to steep hills.
- Efficiency: The right gear can make it easier to ride uphill or against the wind and can increase speed on flat or downhill stretches.

Basic Components
- Chainrings: These are the big rings attached to the pedals. Bikes can have one, two, or even three chainrings.
- Cogs: Located on the rear wheel’s hub, these form the cassette. A bike might have anywhere from 7 to 12 cogs in the cassette.
- Chain: Connects the chainrings and cogs, transferring pedal power to the rear wheel.
- Derailleurs: Mechanical devices that move the chain from one gear to another.
Types of Gearing Systems
- Derailleur gears: The most common system on many bikes. It operates by moving the chain between different-sized cogs and chainrings.
- Internal hub gears: These gears are enclosed within the rear hub of the bike. They’re low maintenance and good for city bikes or cruisers.
- Fixed gear (“fixie”): No gear shifting. The bike has only one gear. Popular among city riders and track cyclists for their simplicity.
- Single speed: Like a fixie but has a freewheel, so you can coast without pedaling.
Gear Ratios
This refers to the relationship between the front chainring size and the rear cog size. For instance, a 2:1 gear ratio means for every two revolutions of the pedals, the rear wheel turns once.
A lower gear ratio (like 1:1) makes it easier to pedal uphill but is slower. A higher gear ratio (like 3:1) is harder to pedal but faster.
Shifting Gears
- Shifters: Located on the handlebars, they control the derailleurs. There are different styles including trigger shifters, twist shifters and integrated brake-shifters.
- Tips for Smooth Shifting: Always pedal lightly when shifting, shift sequentially and try to anticipate terrain changes.

Bike gears play a crucial role in optimizing the efficiency and versatility of a bicycle. Whether one is a casual rider, mountain biker, or road cyclist, understanding and correctly utilizing gears can greatly enhance the cycling experience.
Types of Bike Gear Shifters
Bicycle gear shifters are the components that allow riders to change gears. There are various types of shifters available, each with its own design and method of operation. Here’s a breakdown of the main types:
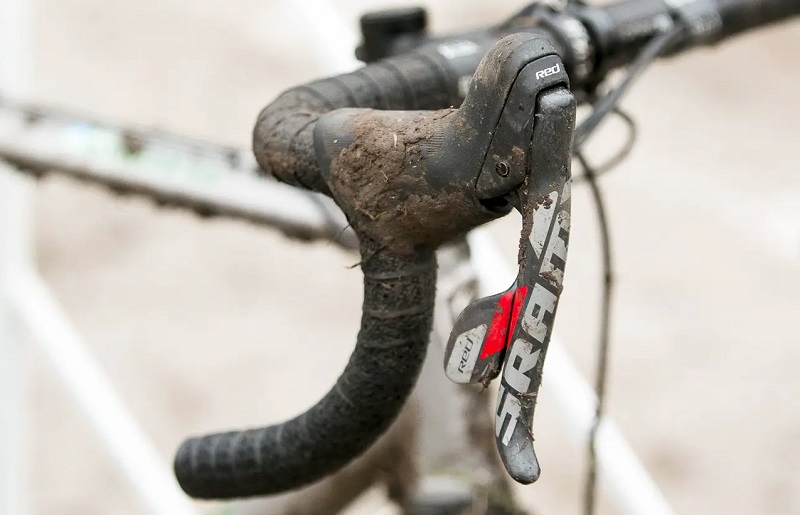
Friction Shifters
Friction shifters are one of the oldest types of gear shifters and operate manually. They allow the rider to move the derailleur by controlling a lever, which tightens or loosens a cable.
Advantages:
- Gives the rider complete control.
- Simplicity in design, making them durable.
Disadvantages:
- Requires more skill to get accurate gear changes.
- Might not be suitable for beginners due to the manual adjustment needed.
See more: What do the different gears on a bike mean?
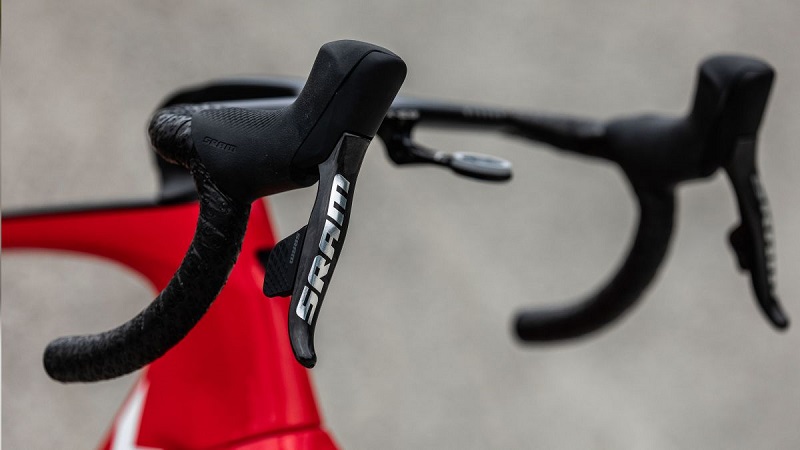

Indexed Shifters
Indexed shifters offer a more modern approach. With each click or push of a button, the shifter moves the chain to a specific gear.
Advantages:
- Ensures precise and consistent gear shifts.
- Easier for beginners to understand and use.
Disadvantages:
- Might not offer the same level of fine-tuning as friction shifters.
- Can get misaligned if not regularly maintained.
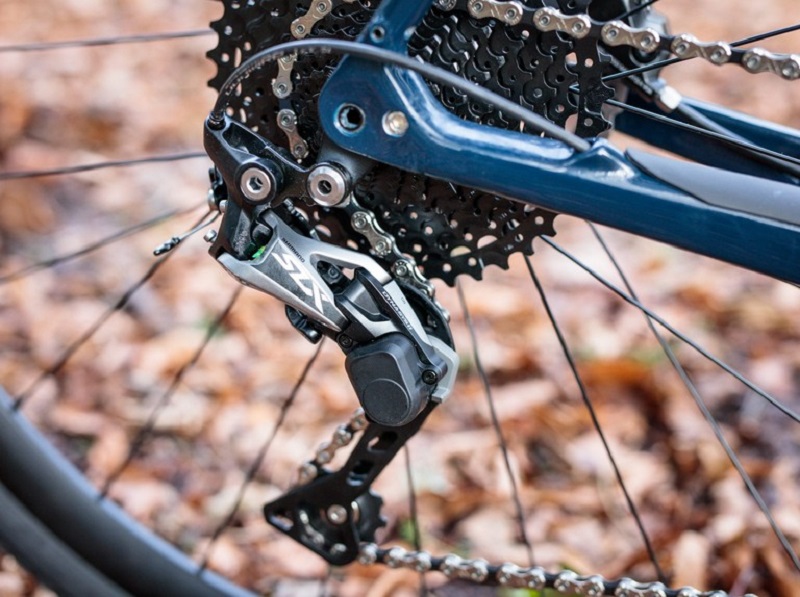
Trigger Shifters
Found mostly on mountain bikes, trigger shifters have two levers: one for upshifting and another for downshifting. The thumb usually operates them.
Advantages:
- Quick and accurate shifting.
- Ergonomically designed for comfort.
Disadvantages:
- Might be challenging to use with gloves during colder seasons.
- Can be more complex than other systems.

Grip Shifters
As the name suggests, grip shifters require the rider to twist a section of the handlebar grip to change gears.
Advantages:
- Simple and intuitive to use.
- Compact design that integrates seamlessly with the handlebars.
Disadvantages:
- Can accidentally shift gears if the grip is not held correctly.
- Might not be as durable as other types.
Bar End Shifters
Installed at the ends of drop bars, these shifters work by pushing them in and out or rotating them.
Advantages:
- Offers both indexed and friction shifting.
- Durable and requires minimal maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- Not the best choice for fast-paced cycling like racing.
- Position can be uncomfortable for some riders.
Electronic Shifters
Electronic shifters represent the pinnacle of modern gear shifting technology. They operate using electric signals rather than cables.
Advantages:
- Provides precise and lightning-fast gear changes.
- Reduces manual errors.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than mechanical systems.
- Requires batteries or charging.
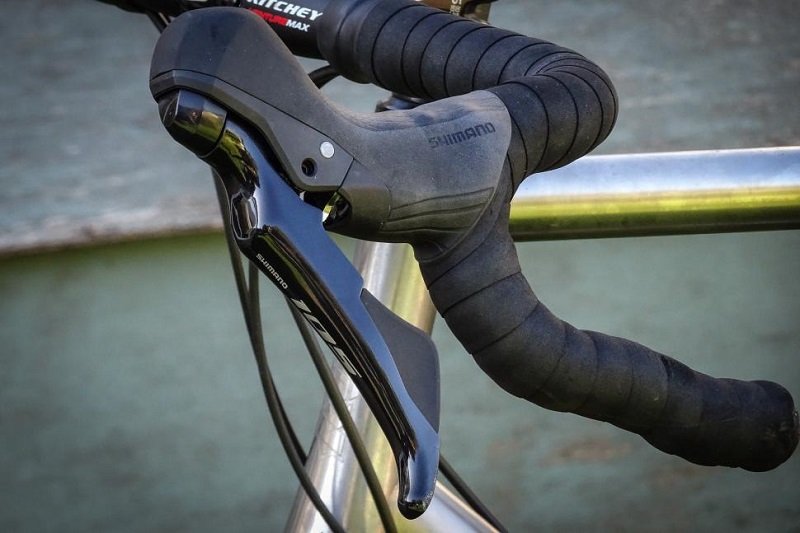

When selecting a type of gear shifter, it’s essential to consider the type of riding you plan to do, the kind of bike you have and your personal preferences for gear changing. Each shifter type offers a different experience and can influence how you interact with your bike’s gearing system.
How to Choose the Right Gear Shifter for Your Bike?
Choosing the right gear shifter for your bike involves considering several factors related to your riding style, bike type and personal preferences. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
Type of Riding
- Mountain Biking: Trigger shifters are popular due to their quick response and the ability to shift multiple gears at once. Electronic shifters are also gaining traction in high-end mountain bikes for their precision.
- Road Cycling: Integrated brake-shifters (brifters) are standard because they allow for shifting without moving hands from the braking position. Electronic shifters are popular in the high-end segment.
- Touring: Bar-end shifters are a favorite because of their simplicity and durability. Downtube shifters are also an option for those who prefer a retro feel.
- Commuting/City Riding: Internal hub shifters offer simplicity and the ability to change gears while stationary. Twist shifters are also common on city bikes.
See more: Is gear 1 high or low on a bike?

Compatibility
Ensure that the shifter is compatible with your bike’s drivetrain. The number of gears (cogs) on your rear cassette and the type of front derailleur system (if you have one) will dictate which shifters you can use.
For example, a 10-speed rear cassette requires a 10-speed shifter. Check compatibility between brands. While many components are interchangeable, some brands/designs are proprietary.
Mechanical vs. Electronic
Mechanical Shifters: Operate via a physical cable to change gears. They’re generally more affordable, easy to maintain and repairable in most settings.
Electronic Shifters: Use battery-powered motors for gear changes. They’re precise and offer consistent shifting but are pricier and rely on battery power.
Ergonomics & Comfort
Consider the feel of the shifter in your hand. Some riders might prefer the tactile feedback of a trigger shifter, while others might favor the seamless twist of a grip shifter.
Look at the positioning: A shifter should be within easy reach and not require awkward hand movements.
Durability & Maintenance
If you often ride in harsh conditions (mud, rain, etc.), you’ll want a robust and easily maintained shifter.
Electronic systems, while durable, may require professional servicing. Mechanical systems can often be maintained with basic bike repair knowledge.
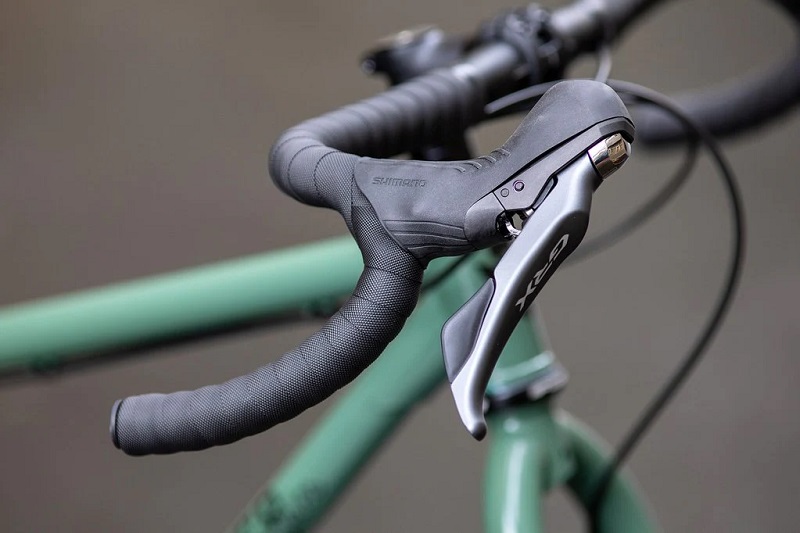

Budget
Shifters range from affordable basic models to high-end, feature-rich versions. Determine what features are essential for you and what you’re willing to invest in your bike’s shifting system.
The right shifter can enhance your cycling experience, providing seamless gear changes and improved efficiency. By considering your needs and preferences, you can find a shifter that’s perfect for your bike and riding style.
Conclusion
Understanding the various Bike Gear Shifter Types is essential for both beginners and seasoned cyclists. It allows riders to harness the full potential of their bikes, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable ride irrespective of the terrain. As cycling technology continues to advance, it’s vital to stay updated and choose the best gear shifting system that aligns with your cycling goals.