Parts
Bike Frame Parts: Name with Picture
Cycling enthusiasts, professional racers, and everyday bike riders understand the significance of a well-built bike. The bike frame forms the foundation of any bicycle and plays an instrumental role in determining its performance, strength, and longevity. In this comprehensive guide, HookBike’s shall delve deep into the intricacies of Bike Frame Parts, accompanied by names and pictures, ensuring that you become well-versed with every component.
The Essential Parts of a Bike Frame
The frame is the backbone of a bicycle; it’s the component to which all other parts are attached, and it plays a crucial role in determining the bike’s ride characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of the essential parts of a typical bike frame:
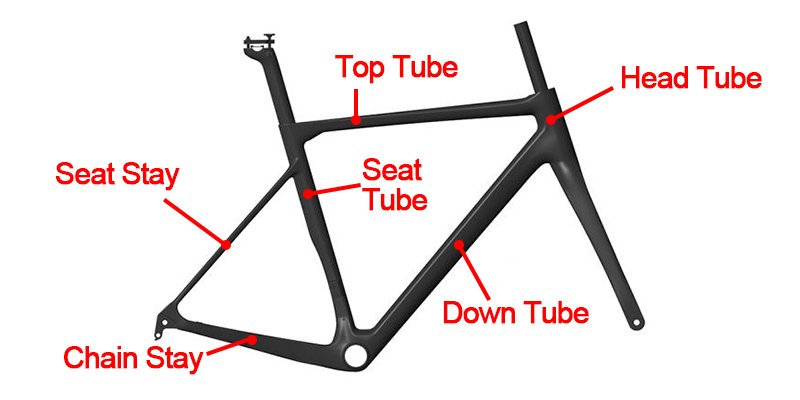
Head Tube
The head tube is the front-facing part of the bike frame, responsible for holding the handlebars and the front fork. It’s crucial for steering and dictates the bike’s responsiveness when navigating corners or dodging obstacles.
Top Tube
Connecting the head tube to the seat tube, the top tube is a horizontal bar that provides structural integrity. It’s particularly significant for determining the bike’s size and fit for the rider.
Down Tube
The down tube is the section that connects the head tube to the bottom bracket shell. This component plays a pivotal role in transferring power and energy from the rider to the bicycle’s wheels.
Seat Tube
This vertical component holds the seat post and the saddle. It’s essential for determining the height of the bike and can be adjusted to ensure optimal riding comfort.
Seat Stay
Extending from the seat tube to the rear dropouts, the seat stay provides rear wheel support and contributes to the bike’s overall stability and shock absorption.
Chain Stay
The chain stay runs parallel to the chain, connecting the bottom bracket shell to the rear dropouts. It keeps the chain in place and is crucial for the power transfer between the pedal and the rear wheel.
Bottom Bracket Shell
Situated at the bicycle’s base, this part houses the bottom bracket and connects the down tube, seat tube, and chain stays. It’s a hub of sorts, ensuring smooth pedaling and efficient power transfer.
Dropout
These are small notches or slots at the end of the fork and rear chain stays. Dropouts hold the front and rear wheels in place, ensuring the bike’s stability and safety.
Seat Post Clamp
As the name suggests, this component clamps onto the top of the seat tube and secures the seat post. It allows for easy adjustment of the saddle’s height, ensuring a comfortable ride.
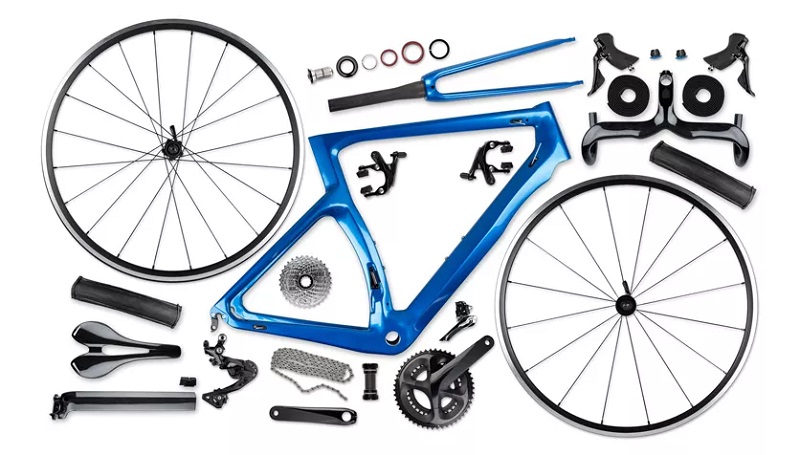
Frame designs can vary based on the type of bicycle (mountain, road, hybrid, BMX, etc.) and the specific needs or characteristics desired (e.g., aerodynamics, comfort, stiffness). The materials used for frames can also vary, from steel to aluminum, carbon fiber, and titanium, each offering different ride qualities and characteristics.
The most popular material for making bike frame parts
Bicycle frames are constructed from a variety of materials, each with its unique set of properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Over the years, some materials have gained popularity due to advances in technology, manufacturing methods, or specific cycling disciplines’ needs. The most popular materials for making bike frames are:
Steel
- Pros: Durable, repairable, offers a smooth ride quality, relatively inexpensive for basic steel alloys.
- Cons: Heavier than aluminum and carbon fiber, can rust if not properly cared for.
- Varieties: High-tensile steel (heavier and more affordable) and chromoly (CrMo) steel (lighter, more responsive, and stronger).
Aluminum (or Aluminium)
- Pros: Lightweight, rust-resistant, stiffer than steel, relatively affordable, easy to work with in manufacturing.
- Cons: Can be harsher in ride quality (though modern designs and engineering have mitigated this), less fatigue life compared to steel.
- Varieties: There are different alloys like 6061 and 7005, with varied properties in strength, weight, and flexibility.
Carbon Fiber
- Pros: Very lightweight, can be engineered to specific stiffness or compliance in different parts of the frame, offers a smooth ride quality, doesn’t corrode.
- Cons: Expensive, can be less durable in direct impacts, damage might be hidden.
Titanium
- Pros: Combines the best properties of steel (ride quality and durability) with the lightness close to aluminum, highly corrosion-resistant.
- Cons: Expensive, requires specialized welding techniques.
- Varieties: Common alloys include 3Al-2.5V and 6Al-4V.
Bamboo (less common but gaining popularity in niche markets)
- Pros: Sustainable, offers unique vibration damping properties, each frame can be unique.
- Cons: Not as universally durable or robust as metal or carbon frames, usually paired with carbon or metal joints.
Thermoplastics (emerging material in specific market segments)
- Pros: Possibility for recyclability, unique design potentials.
- Cons: Not as widespread or time-tested as other materials.
See more: bike frame size chart

Of these materials, aluminum and carbon fiber are arguably the most popular in the modern bike industry:
- Aluminum is prevalent in entry to mid-level bikes due to its balance of weight, strength, and cost.
- Carbon fiber dominates the high-end market, especially in road cycling and mountain biking, because of its weight-saving properties and the ability to fine-tune its characteristics.
However, the “best” material often depends on the specific needs of the rider, the type of riding, budget considerations, and personal preferences regarding ride quality and aesthetics.
Understanding the Importance of Each Part
Each part of the bike frame plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, ride quality, and safety of the bicycle. Let’s delve into the importance of each essential frame component:
Strength and Durability
Each part of the bike frame has its unique role in ensuring that the bicycle remains strong and durable. The materials, design, and quality of these parts influence the bike’s longevity and its performance on various terrains.
Riding Comfort
The bike frame’s design and its parts directly impact the comfort level during rides. Proper alignment, size, and fit play a pivotal role in ensuring that the rider remains comfortable, even during extended cycling sessions.
Efficient Power Transfer
A well-constructed bike frame, with its intricately connected parts, ensures that the energy exerted by the rider is efficiently transferred to the wheels. This results in optimal speed, agility, and responsiveness during rides.
Safety
Each component, from the head tube to the dropouts, plays an instrumental role in the bike’s safety. Ensuring that these parts are of the highest quality, properly maintained, and rightly aligned guarantees a safe cycling experience.
See more: how do you measure a bike frame

Each part of the frame has been refined over decades (and in some cases, over a century) of bicycle design and engineering. While some parts might seem minor, each contributes to the overall function, feel, and safety of the bicycle. When selecting or designing a bike, understanding the role of each component can help in tailoring the bicycle to the rider’s specific needs and preferences.
Conclusion
The marvel of engineering that is a bicycle relies heavily on its frame. Understanding the names and purposes of each component is essential, not just for the cycling enthusiast but for anyone who wishes to ensure their bike is in top condition. A deep dive into the Bike Frame Parts: Name with Picture not only enhances one’s knowledge but also instills a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship behind this two-wheeled wonder.